

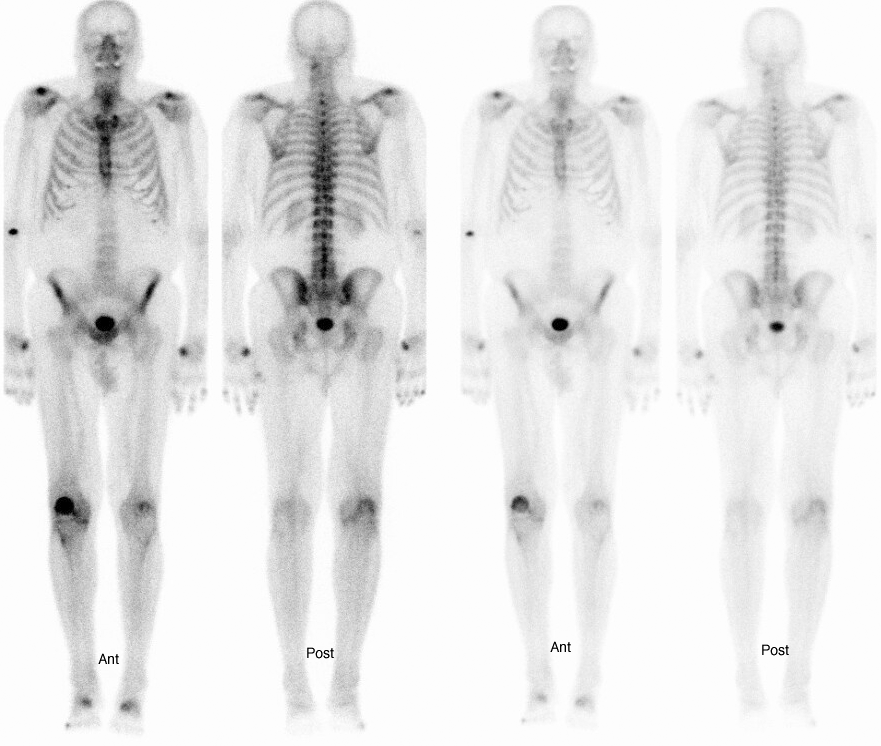
Bone Scan:
A bone scan is carried out to find out the bone problems in the body. It also helps to determine the bone metabolism. Apart from this, a bone scan helps you to find out whether the cancerous cells have spread from bones to any part of the body.
The bone scan process:
A radioactive dye will be injected into the bones during the scan process. The doctor will then monitor you for several hours. The radioactive dye will be completely removed the body within two to three days.
Risks of a bone scan:
It is equivalent to a conventional x-ray. The tracers in the radioactive color utilized as a part of a bone output create almost no radiation. Indeed, even the danger of having a hypersensitive response to the tracers is low.
But, the test might be risky for pregnant or breast feeding ladies. There is a danger of harm to the baby and breast milk might get contaminated. Try to tell your specialist in case you're pregnant or are breast- feeding.
Preparing for a bone scan:
A bone sweep requires no unique arrangement. Prior to the sweep, your specialist will request that you take off the metal jewelery from your body.
The genuine screening methodology takes around 60 minutes. Your specialist may give you a gentle narcotic to help you relax if you are unable to sit for a longer period of time.
How Is a Bone Scan Performed?
The technique starts with an infusion of radioactive color in your arm. The color is then permitted to work its way through your body for the following two to four hours. Depending on the reason for your bone scan, the doctor will carry out the imaging test.
As the color spreads through your body, the bone's cells actually incline toward regions that need repair. The color's radioactive tracers go after these cells and gather in spots where the bone is harmed.
Sufficiently after time has passed, your specialist will utilize a unique camera to filter the bones. The harmed regions — where the color has settled — show up as dull spots on the picture.
Your doctor will repeat the process if there wasn’t any conclusion in the first round. They may likewise arrange a solitary photon discharge registered tomography (SPECT). This is like a bone sweep, with the exception of the imaging procedure makes 3-D pictures of your bones. A SPECT is fundamental if your specialist needs to see further into your bones. They may likewise utilize it if the first pictures weren't clear in specific regions.
The results:
The tests are normal if the dye is spread evenly and the tests are abnormal if the dye shows the darker spots.